The dream of earning money while you sleep isn’t just a fantasy; it’s a financial strategy that millions of Americans use to build wealth and secure their future. For many, that strategy centers on dividend investing for passive income. While it may seem complex, building a passive income stream through dividends is a straightforward process when you have a clear plan. This comprehensive guide will cut through the jargon and provide a detailed, step-by-step roadmap for anyone in the USA looking to begin their journey with dividend investing for passive income.
From understanding the fundamental concepts to building a diversified portfolio and avoiding common mistakes, we will cover everything you need to start generating a consistent cash flow that can supplement your income or fund your retirement.
Key Takeaways
- Learn the basics of dividend investing for passive income.
- Find out how to choose the right dividend stocks for you.
- See why it’s important to have a mix of stocks in your portfolio.
- Start building a dividend-focused portfolio.
- Make your returns bigger by taking less risk.
- Understanding Dividend Investing
What is a Dividend?
A dividend refers to the distribution of a part of earnings/ profits to shareholders by the decision of the board of directors of the company. It is sort of like your share of the profits. When the company makes a good profit and has excellent cash flow, it shares some of this profit with its shareholders in the form of dividends, which could be cash, stock, or other assets. Dividend investing could be a way to earn while you sleep and make money without much work.
Key Metrics for Dividend Investors
Dividend Yield:
This is the dividend per share divided by the current price of the stock. This is expressed as a percentage and tells you how much passive income you are expected to receive in relation to the stock price. Thus, a company paying out $1.00 a year in dividends with the stock priced at $20 has a dividend yield of 5 percent.
Dividend Payout Ratio:
This is the percentage of company earnings that are paid out as dividends. A lower payout ratio (for example, 50%) suggests that the company has enough room to keep paying dividends and possibly grow them as well. A very high payout ratio (90 percent +) is a red flag, as it could mean that the dividend is not sustainable.
Dividend Growth:
Look for companies that consistently raise dividends to their shareholders over time. This will be proof of the existence of a strong, financially healthy business.
The Power of Reinvestment (DRIPs)
One of the most powerful aspects of dividend investing is the ability to automatically reinvest your dividends back into the same stock or fund. This is called a Dividend Reinvestment Plan (DRIP). Reinvesting your dividends allows you to purchase more shares, which in turn generate additional dividends, creating a compounding cycle that enhances your portfolio’s growth.
The Core Benefits of Dividend Investing
Dividends can give you a steady income. This is ideal for those investors who are seeking regular income.
1. Consistent Passive Cash Flow
Unlike growth stocks that only provide a return when you sell them, dividend stocks provide regular income, often quarterly, that you can use to supplement your lifestyle or pay bills.
2. Protection from Inflation
By investing in companies that increase the dividend, you will have an advantage to continue augmenting the stream of passive income close to or over inflationary levels, thus protecting purchasing power.
3. Cushion in a Down Market
In a down market, your stock prices may fall, but your dividend payments can remain steady or even continue to grow. This consistent income can provide a sense of stability and reassurance during periods of market volatility.
4. Potential for Capital Appreciation
While targeting income, many quality dividend-paying companies are financially sound businesses that also have the potential for their stock price to increase over time. This gives you a dual benefit of income and growth.
5. Generate Passive Income and The Cash Flow Advantage
Dividends can give you a steady income. Dividend stocks can give you a passive income. These are handy for investors who depend on that kind of cash flow.
6. Long-term Wealth Building
Wealth-building depends on the reinvestment of dividends as an internally generated revenue channel.
7. Supplementing Retirement Income
At this phase in life for many nearing retirement, dividend investment became a wise choice. It adds to your retirement income. By choosing companies that pay steady dividends, you get a stable income for your retirement.
Building a Dividend Portfolio: A Practical Guide for Beginners
Step 1: Open a Brokerage Account
Your first step is to open a brokerage account in the USA. Good options with a reputation that are beginner-friendly are:
- Fidelity
- Charles Schwab
- Vanguard
Step 2. Brokerage Options for Dividend Investors
When selecting the right brokerage, consider factors like fees, account minimums, and investment options. Some platforms cater specifically to dividend stocks and ETFs, whereas others offer a variety of assets and great educational resources. For dividend-oriented investing, find a platform that will charge you the least, if anything, for stock and ETF trades.
There are different account types for different goals. A taxable account is flexible. An IRA offers tax benefits.
Step 3: Start with a Diversified Approach
It would be tempting to invest in a handful of individual stocks. But the greatest way to reduce risk will be through investment diversification. First of all, begin by deciding how much you can invest. You can do it slowly, that is, invest a little and learn slowly, or invest a lump sum at once. Slowly investing gives you valuable hands-on experience. Investing large sums would bring in massive returns if the timing is right. These considerations lead to how much money you invest and your level of risk. Rather than individually picking companies, one should start with dividend-focused ETFs or mutual funds.
Why? These funds hold a large basket of dividend-paying stocks from various sectors, so the poor performance of one company won’t sink your entire portfolio. They are an excellent way to get immediate exposure to a wide range of high-quality dividend payers.
Step 4: Finding and Researching Dividend Investments
When you’re ready to start researching, here’s what to look for:
Quality over Yield: Don’t go chasing after the highest dividend yield. It may mean trouble for a company if it has a sky-high yield. Why? It might mean that the company’s stock price has tanked. Look for a sustainable yield with a history of good payments.
Examine the Payout Ratio: A healthy payout ratio (e.g., under 75% of earnings) indicates that a company can afford its dividend and has room for growth.
Check Payment History: Find out how long a company has been paying and increasing its dividend. A good starting point for your research is the “Dividend Aristocrats” (S&P 500 companies that have increased dividends for at least 25 consecutive years).
Step 5: Setting Clear Income Goals
What do you expect from dividends? Monthly income or growth? Your goals help you choose your investments.
Step 6: Finding Your Time Horizon
Your time horizon commands your strategy. It will be more risk-taking if it’s longer and more risk-averse in a shorter one.
Smart Investment Options for Dividend Income
1. Blue-Chip Dividend Stocks
These are big companies that have established their name, are financially stable, and have a history of declared dividends. They are less volatile than smaller companies. Examples would be large corporations in the consumer staples, utilities, and healthcare sectors.
2. Dividend ETFs and Mutual Funds
This is the recommended starting point for most beginners.
Vanguard High Dividend Yield ETF (VYM): Very popular and with a low expense ratio.
Schwab U.S. Dividend Equity ETF (SCHD): Very much appreciated for the focus on the companies with strong fundamentals and dividend growth.
ProShares S&P 500 Dividend Aristocrats ETF (NOBL): Concentrates on the Dividend Aristocrats, thus providing investment exposure to companies with a long stretch of dividend increases.
3. Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs)
REITs are companies that operate income-producing real estate. They are legally required to pay out at least 90% of their taxable income to shareholders, making them excellent sources of dividend income.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
The “Dividend Trap”:
Watch out for yield traps. These are high yields that come from a stock price going down. This often means the company is having problems. Always check the company’s health before just looking at the yield. Buying a stock solely for its high yield without looking at its fundamentals. A company cutting its dividend can cause its stock price to plummet.
Ignoring Diversification:
Putting all your money into a single sector or a few stocks can leave you vulnerable to a downturn.
Dividend Payout Ratio:
This ratio demonstrates the percentage of earnings distributed to shareholders through dividends. This ratio tells you if the dividends can keep going.
Sustainable vs. Unsustainable Payouts:
An ideal payout ratio should be below 60 percent. This shows that even during bad phases, the company can continue paying dividends. A high payout ratio means the probability of cutting dividends is high.
Dividend Growth Rate:
The dividend growth rate shows how fast dividend payments are growing. A steady increase is a good sign of the company’s health and care for shareholders.
Historical Growth Patterns:
Looking at how dividends have grown over time is important. You want to see a company that keeps raising its dividend payments.
Company Financial Health Indicators:
Checking a company’s financial health is key when picking dividend stocks. Look at debt and cash flow to see if the company can keep paying dividends.
Debt Levels and Cash Flow Analysis:
A company’s debt and cash flow tell you a lot about its financial health. Good cash flow and not too much debt are signs that it can keep paying dividends.
Overlooking Taxes:
Dividends are taxable income. Be sure to understand the difference between qualified and non-qualified dividends and the role of your retirement accounts.
Dividend Reinvestment Strategies
Reinvesting dividends can grow your money over time. It helps your portfolio grow faster. This section will look at how to reinvest dividends.
DRIP Programs Explained
The premises or foundations establishing schemes allowing shareholders to use their dividends in buying more shares automatically are Dividend Reinvestment Plans (DRIPs). There are two paradigms on this front.
Company-Sponsored vs. Brokerage DRIPs
Company-sponsored programs are run by the company itself. They are user-friendly. The broker program works through the broker. They offer more choices.
Manual Reinvestment vs. Automated DRIPs
You can reinvest dividends manually or through automated DRIPs. Automated DRIPs are easy and keep you on track. Manual reinvestment lets you control your investments.
Pros and Cons of Each Approach
- Automated DRIPs: Pros – easy, keeps you disciplined; Cons – less control over when to invest.
- Manual Reinvestment: Pros – more control, flexible; Cons – needs more effort, discipline.
When to Reinvest and When to Take Income
Decide to reinvest or take dividends based on your goals and life stage.
Life Stage Considerations for Dividend Investors
| Life Stage | Reinvestment Strategy |
| Accumulation Phase | Reinvest dividends to maximize growth |
| Retirement | Consider taking dividends as income |
As shown in the table, your strategy should match your life stage and financial goals. In the accumulation phase, reinvesting boosts growth. In retirement, taking dividends as income helps with living costs.
By using these strategies, you can make your investments work better and help you reach your financial goals.
Tax Considerations for Dividend Investors
When you invest in dividends, knowing about taxes is key. The tax on your dividends can change how you invest.
Qualified vs. Non-Qualified Dividends
Dividends are rated as either qualified or non-qualified. Generally, qualified dividends are taxed at a lower rate, similar to that for long-term capital gain, while non-qualified dividends are taxed as ordinary income.
Tax Rate Differences and Holding Requirements
Holding requirements must also be met for obtaining low tax rates. To get the low tax rate, one has to hold shares for a longer period than 60 days in a period of 121 days, which begins 60 days before the ex-dividend date.
Tax-Advantaged Accounts for Dividend Investing
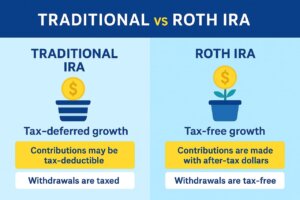
Using tax-advantaged accounts can lower your dividend tax. Accounts like IRAs, 401(k)s, and Roth accounts have tax benefits for dividend investing.
IRAs, 401(k)s, and Roth Accounts
- Traditional IRAs and 401(k)s grow tax-free until you withdraw. Then, you pay taxes.
- Roth IRAs and Roth 401(k)s grow and withdraw tax-free if you meet certain rules.
Tax-Efficient Dividend Portfolio Structuring
Building a smart dividend portfolio can lower your taxes. This means using asset location strategies to place investments wisely.
Asset Location Strategies
For example, put tax-inefficient investments in tax-deferred accounts. This can lower your taxable income.
Conclusion: Creating Lasting Wealth Through Dividend Investing
Dividend investing for passive income is not about getting rich quickly; it’s about building a consistent, long-term strategy for wealth building in the USA. By focusing on quality companies, prioritizing diversification, and consistently reinvesting your dividends, you can build a powerful passive income stream that will work for you for years to come. Remember, the key is patience and consistency. Start small, stay the course, and watch your passive income grow.
New areas like renewable energy and technology also offer good dividends. They can grow your money while giving you income. This makes your portfolio stronger.
This guide has shown you how to pick good dividend stocks. You also learned how to make your portfolio strong and grow your money. Now, you can start your journey in dividend investing.
Keep working on growing your dividend income. This will help you build a strong financial future. You’re on the right path.
FAQ
What is dividend investing, and how can it generate passive income?
Dividends represent shares of the company’s profits paid out to investors for the long-term holding of such shares. With passive income, one can reap the reward of money working for them. This makes dividend investing one way of earning money while people sleep.
First, open an investment account with a brokerage firm. Then choose how much to invest. Third, make an investment plan that details your preferences on dividend investing. Now go on to search for the stock or fund options that suit your investment goals.
Dividend Aristocrats are companies that have continuously increased their dividends for 25 years or more. They are great in that they give profit-sharing to shareholders. They also show stability and solid growth.
The dividend yield, payout ratio, growth rate, and general financial condition of the company are factors you should evaluate. This will assist you in determining both the safety of the dividend payment itself and whether the stock is a worthy investment.
When a dividend is received, it is automatically used to purchase more shares. While this is growing your investment, no extra charges are incurred, which is an intelligent way of making your money work harder.
High-yield dividend-paying investments earn more returns and are well-suited for those wanting regular payouts. But caution is required as high-yield stocks can be riskier investments.
You should distribute your investments across other industries. Have a mix of staples and some new areas, such as real estate. Aim for a balance of growth and income. Be mindful of risk and know when to sell your stocks.